“If you think Compliance is expensive, try
Non-Compliance”

Why It Is Important for Organisation to Follow Compliance?
“Compliance” in the context of cybersecurity and data protection refers to the act of adhering to laws, regulations, industry standards, and contractual obligations that are designed to protect data, systems, and customers.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
These are laws and government-imposed rules that organizations must follow, depending on the regions and industries in which they operate.
Meeting Contractual Requirements
These are obligations agreed upon in contracts with clients, partners, or vendors. They might specify:
- Data protection standards
- Security protocols
- Reporting and auditing obligations
Why Compliance Matters
- Protects data (personal, financial, health, etc.)
- Secures systems from breaches, leaks, or failures
- Protects customers from fraud, identity theft, or misuse of their data
- Avoid legal penalties and reputational damage
- Enables trust with clients, partners, and regulators
How can absence of compliance lead to atrocities for companies or nations?
- McDonald’s Cybersecurity Error – July 14, 2025

More than 64 million McDonald’s job applicants have their personal information exposed thanks to a huge security oversight in an AI chatbot. The issue was highlighted by two security researchers, who managed to crack the chatbot with the password “123456.”
- Kotak Mahendra found non-compliant with RBI’s APRIL 25, 2024
In one of its sternest disciplinary measures against a major institution, the Reserve Bank of India on APRIL 25, 2024, prohibited Kotak Mahindra Bank from issuing new credit cards and onboarding customers via online and mobile banking platforms, citing “serious deficiencies” in the private lender’s IT infrastructure and repeated lapses in addressing these issues.
Essential elements of an effective compliance program?
- Implementing written policies and procedures
- Designating a compliance officer and compliance committee
- Conducting effective training and education
- Developing effective lines of communication
- Conducting internal monitoring and auditing
- Enforcing standards through well-publicized disciplinary guidelines
- Responding promptly to detected problems and undertaking corrective action.
Some major compliance frameworks:


Various Standerds
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Regulates how personal data is collected, processed, and stored within the EU, impacting any organization that handles data of EU residents.
Example: Organisation that deals with data of EU countries. - HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): A US law that protects sensitive patient health information, requiring organizations to implement security measures to safeguard data.
Example: Clinical Research Organisation, Diagnostic Centres etc - PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Sets security standards for organizations that handle payment card information, helping to prevent fraud and data breaches.
Example: Organisation deals with payment card like PayU, Razor pays, Zaak pay etc. - ISO 27001: Information Security Management System: An international standard for information security management, framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an information security management system.
Example: Phonepe, SentinalOne etc
How are regulators driving compliances across the Indian ecosystem?
Indian regulators viz., RBI and SEBI are ensuring a robust cybersecurity setup across the country through a combination of regulatory frameworks, audits, and enforcement actions. They mandate cybersecurity policies, require regular audits, and impose penalties for non-compliance to strengthen the financial sector’s resilience against cyber threats.
RBI’s Approach to Strengthening Cybersecurity:
- RBI Cyber Security Framework for Banks: The RBI has established a comprehensive cybersecurity framework for banks and other financial institutions. This framework includes guidelines for creating a robust cybersecurity policy, implementing controls to manage cyber risks, and establishing mechanisms for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber incidents.
- Incident Reporting and Information Sharing: The RBI has established mechanisms for banks to report cybersecurity incidents promptly and share threat intelligence with each other and regulatory bodies.
SEBI’s Approach to Strengthening Cybersecurity:
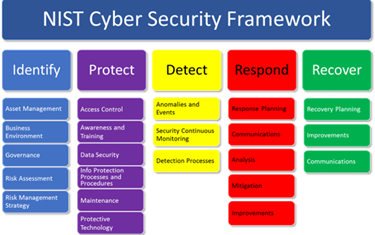
- Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience Framework (CSCRF): SEBI introduced the CSCRF in August 2024 to enhance cybersecurity practices across regulated entities in the Indian securities market, including stock exchanges, depositories, brokers, and mutual funds. This framework emphasizes a holistic approach to cybersecurity, encompassing governance, identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery.
- Compliance Deadlines and Audits: SEBI has set compliance deadlines for regulated entities to adhere to the CSCRF guidelines and mandates periodic cybersecurity audits conducted by CERT-In empanelled auditors to ensure compliance.
Key elements of the cybersecurity Frameworks:
- Governance: Both RBI and SEBI frameworks emphasize the importance of board-level oversight and accountability for cybersecurity. Monitoring Internal Audits periodically checks to verify compliance with policies and detect potential violations or weaknesses. Formal documents that define your organization’s security rules, expectations, and operational guidelines.
- Risk Management: Regulated entities are required to conduct regular risk assessments and implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies. Identifying and evaluating risks to data, systems, and operations, then aligning them with appropriate controls. Risk of Non-compliance can still lead to financial consequences, Legal Consequences, Reputation Loss etc.
- Technology and Infrastructure : The frameworks outline guidelines for implementing robust technological solutions and infrastructure to support cybersecurity efforts, including network security, access controls, and data protection measures.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Regulated entities are expected to have mechanisms in place for rapid detection, response, and recovery from cyber incidents. Plans and processes to detect, contain, respond to, and report security incidents and data breaches.
- Employee Training & Awareness: Ongoing education to ensure staff understand their roles and responsibilities in compliance and security.
- Continuous Improvement: The ongoing cycle of reviewing and enhancing your compliance program based on findings, changes, and feedback.
Compliance is essential for companies and organizations for several reasons:
- Avoiding Legal Penalties: Companies must adhere to a wide range of laws and regulations across different countries and regions. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, legal sanctions, and even criminal charges.
- Protecting Against Financial Losses: Beyond direct penalties, non-compliance can lead to significant financial setbacks due to lawsuits and damage claims. Maintaining compliance helps mitigate these financial risks.
- Preserving Company Reputation: In today’s fast-paced information environment, compliance breaches can severely harm a company’s reputation. Customers, investors, and partners tend to Favor businesses that demonstrate ethical and responsible practices.
- Fostering an Ethical Corporate Culture: Compliance initiatives promote a culture grounded in ethics and lawful conduct, which can boost employee morale and enhance the overall workplace environment.
- Gaining Competitive Advantage: Organizations with robust compliance programs often distinguish themselves as dependable and trustworthy, giving them an edge over competitors in the marketplace.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Implementing compliance procedures can streamline internal processes by standardizing workflows and reducing complexity, ultimately improving operational performance.
- Ensuring Compliance with International Standards: In globally connected industries, adherence to international norms is critical for success. Compliance facilitates conformity with these standards and eases entry into new markets.
- Demonstrating Social Responsibility: Companies hold a societal responsibility, especially concerning environmental sustainability and social justice. Compliance programs support these commitments and enable positive societal contributions.
Conclusion
Compliance is essential for mitigating risks, maintaining trust, and ensuring sustainable growth. Adhering to legal and ethical standards enables organizations to operate effectively, protect their reputation, and meet the demands of an interconnected global market. Ultimately, compliance reflects a company’s commitment to integrity and responsible business practices.











